Hey there, solar enthusiasts! If you’re thinking about going solar in 2025, you’re in good company. More homes and businesses are switching to solar power than ever before, and it’s exciting to see how it’s transforming energy use. But here’s the thing: even with all the advancements, installation slip-ups are still a major headache. They can lead to underwhelming energy output, busted inverters, shorter battery life, and surprise bills that nobody wants.
From what I’ve seen in industry reports, over 40% of new solar setups have at least one big flaw that could have been dodged with a bit more upfront planning and expert advice. It’s frustrating, but the good news is that knowledge is power—literally, in this case.
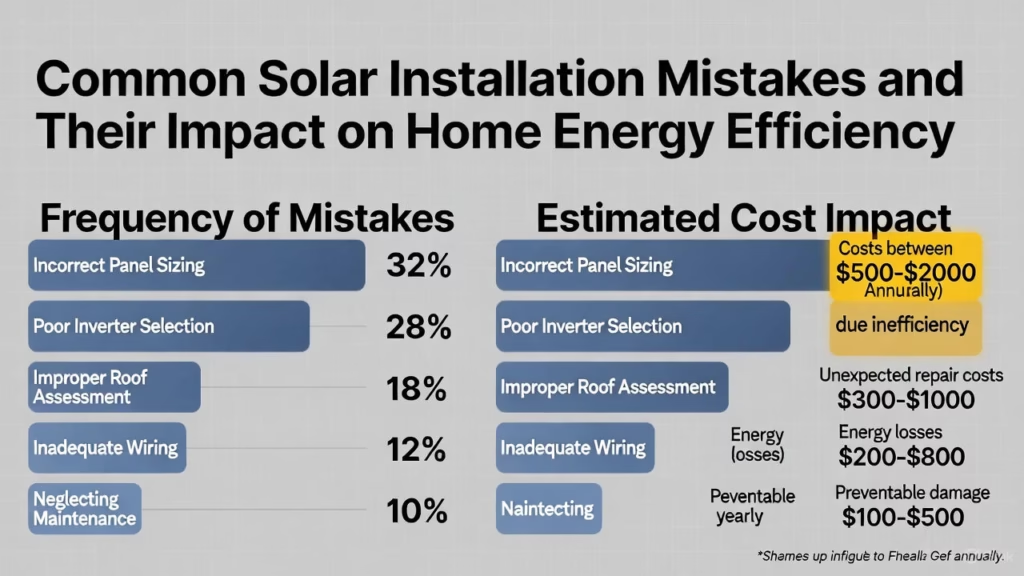
In this in-depth guide, I’ll walk you through the most common pitfalls in solar installations, explain why they happen and what they cost you, and share straightforward tips to steer clear of them. Whether you’re a homeowner dipping your toes into solar, an installer honing your craft, or an engineer geeked out on the tech, there’s something here for you. I’ll even touch on some eye-opening stats and visuals to drive the points home.
Let’s dive in and make sure your solar journey is smooth sailing.
-
Getting the System Size Wrong
Sizing your solar system incorrectly is like buying shoes that don’t fit—it’s uncomfortable and wasteful. This is hands-down the top mistake, often because folks base it on rough guesses instead of real data.
Why It Happens
- Skipping a thorough energy audit of your home or business.
- Falling back on generic rules like “3 kW should do the trick.”
- Forgetting about power spikes from starting up big appliances.
- Not planning for future needs, like adding an EV charger.
- Just copying what your neighbor has without considering your unique setup.
The Fallout
- Your batteries might drain quicker than expected.
- The inverter could overload and trip frequently.
- Panels won’t generate enough juice to meet demand.
- Components wear out faster, leading to early replacements.
- And worst of all, you’re left disappointed because the system doesn’t deliver as promised.
How to Dodge It
Start with a solid energy audit—track your daily and peak usage. Make a list of every appliance, their wattage, and how long they’re on. Build in a 20-30% buffer for growth. Ensure your panels and batteries sync perfectly with the inverter’s capacity. Tools like online calculators or pros from reputable firms can help nail this down.
-
Mismatching Inverters and Panels
Pairing the wrong inverter with your panels is a recipe for inefficiency. It’s like trying to run a marathon in flip-flops—not going to end well.
Common Slip-Ups
- Panels outputting voltage that’s too high for the inverter’s MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) to handle.
- Not enough panel power to even kickstart the inverter.
- Throwing together panels with different specs in the same array.
What Goes Wrong
- The inverter might not start up or shuts down randomly.
- Efficiency drops, meaning less energy harvested.
- Extra heat builds up, stressing the system.
- In extreme cases, it damages the inverter’s internals.
Prevention Tips
Double-check the MPPT voltage range before wiring anything. Adjust for temperature changes—panels’ open-circuit voltage (Voc) can spike in cold weather. Stick to identical panels per string and leave some headroom for those chilly mornings.
-
Sloppy Wiring and Cable Chaos
Wiring might not be glamorous, but skimping here is asking for trouble. Poor cable management can turn a great system into a fire waiting to happen.
Typical Problems
- Using cables that are too thin for the job.
- Leaving exposed wires or sloppy connections.
- Skipping protective trunking.
- Loose or faulty MC4 connectors.
- Overloading circuit breakers.
The Consequences
- Voltage drops steal your efficiency.
- Hot spots form, raising fire risks.
- Charging slows down.
- The whole system becomes unstable.
Smart Fixes
Opt for PV-rated cables that match your setup. Crimp connectors properly and follow standards like NEC or IEC. Use trunking to keep things neat, and swap out any dodgy breakers. A tidy install is a safe install.
-
Placing Panels in Shady Spots or Wrong Directions
Panels thrive in full sun—shade is their kryptonite. Even a little shadow from a branch or chimney can slash output dramatically.
How It Sneaks In
- Rushed site surveys miss potential issues.
- Mounting behind tall structures.
- Too close to obstacles like water tanks.
- Wrong tilt for your location’s sun path.
The Damage
- Daily energy production tanks by 30-80%.
- Panels degrade quicker.
- MPPT gets thrown off.
- Batteries don’t charge fully.
Avoidance Strategies
Do a detailed shading analysis first—apps and tools can simulate this. Trim trees, relocate if needed, and aim panels south (in places like Nigeria) for max exposure. Optimal tilts? Around 10-15° in many regions. For tricky spots, micro-inverters or optimizers can save the day.
-
Pushing the Inverter Too Hard
It’s tempting to think your inverter can handle anything, but overloading it is a fast track to failure.
Bad Load Examples
- Running a freezer on a tiny 1.5 kVA unit.
- Water pumps, heaters, irons, kettles, or ACs that exceed limits.
What Happens Next
- Frequent overload shutdowns.
- Shorter life for key parts like MOSFETs.
- Heat buildup and potential damage.
How to Stay Safe
Know your inverter’s rating and stick to it. Label inverter-powered outlets clearly. Switch to energy-efficient gadgets, and upgrade if your needs grow.
-
Messing Up Battery Setup
Batteries are the heart of off-grid or hybrid systems, and botching their config can be pricey.
Frequent Errors
- Mixing old and new batteries.
- Sloppy parallel wiring without balancing.
- Using car batteries instead of deep-cycle ones.
- No Battery Management System (BMS) for lithium.
The Risks
- Quick drainage and uneven wear.
- Fire hazards from overcharging.
- Voltage issues harming the inverter.
Best Practices
Use matching batteries all around. Wire per manufacturer guidelines, add a BMS for lithium, and include fuses for safety.
-
Skimping on Grounding and Surge Protection
Grounding isn’t optional—it’s your shield against lightning and shocks. Too many installs cut corners here.
Why It’s Bad
- Equipment gets zapped during storms.
- Shock risks rise.
- System noise affects performance.
Easy Wins
Set up a dedicated grounding system with resistance under 5 ohms. Add surge protectors, bond metal parts, and test it all.
-
Forgetting Overcurrent and Short-Circuit Safeguards
Without protection, your system is vulnerable to meltdowns.
What’s Often Missing
- PV fuses.
- DC isolators.
- Proper breakers.
- Lightning arresters.
Potential Disasters
- Fires, damaged wires, inverter failures.
Protect Yourself
Install all the essentials: fuses, isolators, arresters, and breakers on both AC and DC sides.
-
Faulty Roof Mounting and Structural Goofs
A shaky mount can lead to leaks or flying panels in a storm.
Common Blunders
- Drilling into weak spots.
- No flashing for waterproofing.
- Uneven rail spacing.
- Loose hardware.
- Cheap materials.
The Toll
- Leaky roofs, noisy vibrations, lost panels, shorter system life.
Solid Advice
Use quality kits, add flashing, torque bolts right, and confirm your roof can handle the weight.
-
Overlooking Heat Management
Heat is the enemy of efficiency—components need breathing room.
Impacts
- Inverters die young.
- Panels produce less.
- Batteries lose capacity.
Cooling Tips
Place inverters in shaded, airy spots. Elevate panels, give batteries space, and avoid hot areas.
-
Ignoring Rules and Codes
Compliance isn’t bureaucracy—it’s safety.
Downsides
- Inspection fails, fines, forced shutdowns.
Stay Compliant
Follow NEC, IEC, and local regs. Hire certified pros and use approved gear.
-
Lacking Post-Install Support
Installation is just the start—ongoing care keeps it humming.
Issues
- No monitoring.
- Zero maintenance plan.
- Missing warranties.
Fix It
Add remote monitoring, schedule check-ups, and keep all docs handy.
-
Hiring Unqualified Help
Cheap labor often means expensive fixes.
Why It Bites
- Shoddy work, safety risks, rework bills.
Choose Wisely
Go for certified installers with references. Quality over cut-rate prices.
-
Opting for Knockoffs or Junk Parts
The market’s full of fakes—don’t get burned.
Problems
- Failures everywhere: batteries, panels, inverters.
Smart Shopping
Buy from trusted sources, verify serials, check specs, skip suspiciously cheap deals.
-
Skipping Labels and Docs
Good labeling is like a roadmap for maintenance.
Drawbacks
- Tough troubleshooting, wrong fixes.
Do It Right
Label everything, file diagrams, provide a user manual.
FAQs – Common Solar Installation Mistakes
1. What is the most common mistake people make when installing solar?
The biggest mistake is installing a system without proper load assessment. When the system is undersized, the inverter overloads, the battery drains quickly, and expected performance is never achieved.
2. Why does my solar panel produce less power than expected?
Poor placement—especially shading, wrong tilt, or wrong orientation—is usually the reason. Even partial shade on a single panel can reduce total output by up to 80%.
3. Can wrong wiring damage my solar system?
Yes. Undersized cables, loose MC4 connectors, and poor terminations lead to overheating, power loss, and in serious cases, electrical fires. Wiring issues are one of the top causes of inverter shutdowns.
4. Is it safe to mix different battery types or ages?
No. Mixing batteries of different ages, brands, or capacities causes uneven charging, early failure, and can damage the inverter. Always use identical batteries with the same specifications.
5. Why does my inverter keep tripping or shutting down?
This happens when the inverter is overloaded or paired with mismatched panels. Incorrect voltage, wrong panel configuration, or too many appliances cause frequent shutdowns.
6. Do I need surge protection in a solar installation?
Absolutely. Lack of proper earthing and surge protection exposes your system to lightning and voltage spikes, which can destroy panels, inverters, and charge controllers. A dedicated SPD and good grounding are essential.
Wrapping It Up
Solar is an awesome investment for the long haul, but dodging these mistakes is key to reaping the rewards: top-notch efficiency, durable batteries, fewer repairs, safer setup, and better ROI. If you’re gearing up for solar in 2025, take these tips to heart. Chat with experts, plan meticulously, and enjoy the sunny side of energy independence.
Got questions? Drop them in the comments—let’s keep the conversation going!