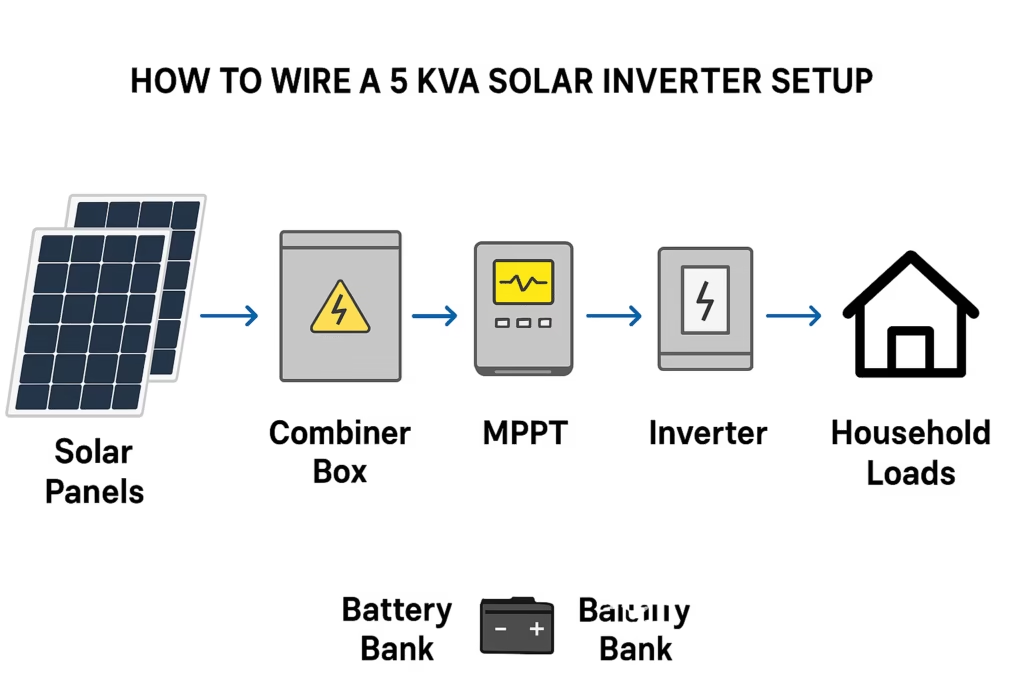
If your wiring is wrong, the system fails. This guide shows the exact wiring order for a reliable 5 kVA solar inverter setup. You get tables, cable sizes, breaker choices, a load planner and schema-ready FAQs. Follow the steps and wire your system the right way.
What this article covers
- The wiring architecture for a typical 5 kVA solar system
- Component list and recommended specs
- Step-by-step wiring instructions with diagrams
- Cable sizing and breaker recommendations
- Sample load planner and runtime estimates
- FAQ schema for search rich results
Required components
Use this table as a reference for a 5 kVA installation.
| Component | Recommended Specs |
|---|---|
| Solar panels | 6–12 panels of 450W to 550W total array 3.3 kW to 6.6 kW |
| Charge controller | MPPT 80A–120A depending on array |
| Inverter | 5 kVA pure sine wave, 48V DC input |
| Batteries | 4×12V in series for a 48V bank or 48V lithium unit |
| Combiner box | With PV breakers and surge protection |
| Breakers | DC breakers on PV strings, DC breaker between battery and inverter, AC breaker on inverter output |
How the wiring works
Follow this order when wiring a reliable 5 kVA system.
- Wire panels in series and parallel as planned
- Bring strings to the combiner box and fit PV breakers
- Run short runs to the MPPT using correct cable size
- Connect MPPT outputs to the battery bank with heavy cable
- Run battery positive and negative to the inverter DC terminals via a DC breaker
- Wire inverter AC output to the distribution board through an AC breaker and changeover switch
Panel stringing options
Series raises voltage. Parallel raises current. Match array voltage to MPPT input window.
| Configuration | Use case |
|---|---|
| 3 panels in series | Higher voltage, lower current. Good for MPPT efficiency. |
| Multiple strings in parallel | Increase power while keeping string voltage within MPPT limits. |
Wiring steps with details
Step 1: Connect your solar panels
Plan the number of panels per string so the maximum voltage stays within the MPPT safe range. Keep string lengths equal.
Step 2: Route panels to the combiner box
Use a combiner box to group strings. Fit PV breakers. Fit a surge protective device and an earth bus.
Step 3: Combiner to MPPT
Use 6mm² to 10mm² copper PV cable for typical strings. Keep cable runs short.
Step 4: MPPT to battery
Use 25mm² to 35mm² battery cable. Connect positive and negative securely. Use a battery isolator if required.
Step 5: Battery to inverter
Use 35mm² to 50mm² between the battery and inverter. Fit a DC breaker sized to the inverter draw between them.
Step 6: Inverter AC output to DB
Wire the inverter output to the distribution board through a double pole breaker. Fit a changeover or automatic transfer switch where needed.
Step 7: Grid input
If the inverter has a grid input, wire the grid via a breaker to the inverter AC input. Set the inverter charger settings before use.
Step 8: Earthing and bonding
Bond all earths. Use a driven earth rod. Link inverter, battery and PV module frames to the common earth.
Cable sizing quick reference
| Section | Recommended cable |
|---|---|
| Solar strings | 4mm² to 6mm² |
| Combiner to MPPT | 6mm² to 10mm² |
| MPPT to battery | 25mm² to 35mm² |
| Battery to inverter | 35mm² to 50mm² |
| Inverter AC output | 4mm² to 6mm² depending on distance |
Short runs reduce voltage drop. Use copper cable and quality terminals.
Sample load planner
Plan loads to keep the inverter stable. Here is a sample for basic household use.
| Appliance | Qty | Wattage | Total (W) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LED bulbs | 10 | 10 | 100 |
| TVs | 2 | 70 | 140 |
| Fans | 3 | 65 | 195 |
| Laptop | 1 | 60 | 60 |
| Router | 1 | 15 | 15 |
| Fridge | 1 | 120 | 120 |
| Total | 630 W |
Common wiring mistakes
- Loose battery terminals
- Reverse polarity on DC connections
- Wrong sized breakers or cables
- Mixing old and new batteries in the same bank
- Long cable runs without accounting for voltage drop
Runtime estimates
Runtime depends on battery capacity. Use this guide to estimate.
| Battery usable capacity | Estimated runtime at 630 W |
|---|---|
| 2.4 kWh | 1 to 2 hours |
| 4.8 kWh | 3 to 4 hours |
| 9.6 kWh | 6 to 8 hours |
| 14 kWh | 10 to 12 hours |
FAQ
How many panels do I need for a 5 kVA inverter?
You usually need 6 to 12 panels depending on panel wattage, daily load demand and available sunlight. A 5 kVA inverter works well with 400W to 550W panels, giving 2.4 kW to 6.6 kW of solar capacity. Choose more panels if you want faster battery charging or stronger daytime support.
What battery size is best for a 5 kVA setup?
A 48V battery bank with 5 kWh to 14 kWh usable energy fits most homes. A 5 kWh bank supports basic nighttime loads. A 10 kWh bank works for homes with fans, TVs and routers. A 14 kWh bank supports heavier use or a small AC at night. Pick a size that matches your daily discharge and how fast your panels can recharge it.
What cable size should I use for a 5 kVA inverter?
Use 35mm² to 50mm² copper cables for the DC battery link because the current is high on the 48V side. Use 4mm² to 6mm² cables for AC output to the distribution board. Keep cable runs short to limit voltage drop and follow regional wiring rules.
Can I run an AC on a 5 kVA inverter?
You can run a small split AC when your solar array and battery bank are big enough to support the starting surge and continuous power draw. A 1 HP or 1.5 HP inverter AC runs well when the battery is almost full and solar input is strong.