What if your monthly electric bill disappeared—yet hidden costs waited in the fine print? This article reveals the lesser-known truths about home solar panels, separating fact from hype. You’ll discover the myths versus realities, understand the real costs and long-term savings, and learn how solar impacts the environment. We’ll also explore government incentives, walk through the installation process, and share essential maintenance tips to help you decide if solar is right for your home.
So, do home solar panels truly live up to the hype? Many homeowners are drawn by the promise of lower bills and energy independence, while others remain cautious about the uncertainties. Let’s dive deeper to uncover the full picture—before you make the switch.
Bust Common Myths
Sales pitches often highlight the benefits of solar but overlook key realities—so it’s important to know the facts. Solar panels continue to generate power even on cloudy days by capturing diffuse sunlight; in places like Seattle, systems still achieve about 70–80% of their rated annual output. When installed correctly, panels do not damage roofs—professional installers use sealed mounting systems, and long-term users report excellent performance, with one California homeowner noting zero leaks after a decade. Efficiency has also improved dramatically, with modern panels converting 20–22% of sunlight into electricity, compared to just 15% in 2010.
Durability is another strong point: most panels last 25–30 years and come with warranties that protect against performance degradation. Cold climates pose no problem either—snow tends to slide off tilted panels, and cooler temperatures can actually boost efficiency by 0.3–0.5% per degree below 25°C. Batteries, while useful for energy storage, are not mandatory since grid-tied systems allow homeowners to sell excess power back to the utility. And if cost seems like a barrier, consider this: solar panel prices have dropped by roughly 60% since 2010, making solar more affordable and practical than ever.
Weigh Pros and Cons
Balance benefits against drawbacks. Make informed choices.
Pros:
- Slash bills. Average US home saves $1,500 yearly on electricity.
- Hedge inflation. Lock in rates as utility costs rise 3-5% annually.
- Boost home value. Add $20,000 to resale price for a $15,000 system.
- Cut emissions. Offset 100 tons of CO2 over lifetime.
- Gain independence. Power outages hit less hard with batteries.
Cons:
- High upfront cost. Systems run $18,000-$43,000 before incentives.
- Maintenance needs. Clean panels twice yearly to keep 95% efficiency.
- Roof space limits. Need 300-500 sq ft for average setup.
- Payback takes time. 6-10 years in sunny states.
- Manufacturing impacts environment. Uses energy and water.
Which side tips the scale for you? Factor your location.
Calculate Real Costs
Numbers matter. Break them down.
Average US install: $29,360 for 10kW system in 2025.
Per panel: $1,200 installed.
Breakdown:
- Panels: 40% of total.
- Inverter: 10-15%.
- Labor: 20%.
- Permits: 5-10%.
Add batteries? Extra $10,000-$20,000.
Financing options: Loans at 4-6% interest.
What fits your budget? Shop quotes from three installers.
Unlock Savings Potential
Solar panels deliver impressive returns over time, with data clearly showing their long-term value. Homeowners typically save between $1,000 and $2,000 annually, depending on energy consumption and local rates. For instance, in Virginia, a standard 5kW solar system can save around $24,433 over 20 years. Most installations reach full payback in about seven years, after which the savings continue to grow. For a $20,000 system generating $1,500 in yearly savings, the cumulative financial benefit becomes substantial—demonstrating why solar remains one of the smartest energy investments available today.
| Year | Cumulative Savings (USD) |
|---|---|
| 1 | -18,500 |
| 2 | -17,000 |
| 3 | -15,500 |
| 4 | -14,000 |
| 5 | -12,500 |
| 6 | -11,000 |
| 7 | -9,500 |
| 8 | -8,000 |
| 9 | -6,500 |
| 10 | -5,000 |
| 11 | -3,500 |
| 12 | -2,000 |
| 13 | -500 |
| 14 | 1,000 |
| 15 | 2,500 |
| 16 | 4,000 |
| 17 | 5,500 |
| 18 | 7,000 |
| 19 | 8,500 |
| 20 | 10,000 |
| 21 | 11,500 |
| 22 | 13,000 |
| 23 | 14,500 |
| 24 | 16,000 |
| 25 | 17,500 |
Savings turn positive after year 13. Extend to 25 years for panels’ life.
Track your usage. Use apps to monitor output.
Claim Incentives Now
Government incentives can dramatically reduce the cost of going solar—but it’s wise to act before policies change. The federal solar tax credit currently offers 30% off installation costs through 2032, meaning a $30,000 system could earn you a $9,000 credit. Many states also provide additional rebates and benefits; for example, Texas grants property tax exemptions for solar-equipped homes. Net metering programs let homeowners sell excess power back to the grid, with unused credits rolling over month to month. Some utility companies even pay as much as $0.10 per kilowatt-hour generated. To find out if you qualify, check the IRS website or contact your local utility provider. Keep in mind that some incentives may decrease after 2025—so installing sooner can lock in greater savings.
Face Environmental Realities
While solar energy significantly cuts pollution over the long term, the manufacturing process tells a more complex story. Producing solar panels requires silicon mining and consumes large amounts of energy—often equivalent to one to four years of a panel’s own power output. The process also uses considerable water, particularly for wafer cleaning, and involves hazardous chemicals like cadmium in thin-film panels that must be handled with care. Although up to 90% of a solar panel’s materials are recyclable, improper disposal in landfills poses toxic waste risks. Still, solar power remains far cleaner than coal, preventing an estimated 50 to 100 tons of CO₂ emissions per household over its lifespan. With growing recycling programs and manufacturers offering take-back schemes for old panels, the industry continues to move toward sustainability. The key question is whether the net environmental benefits outweigh the upfront impacts—a balance that improves when consumers choose eco-conscious brands with low-carbon manufacturing footprints.
Follow Installation Steps
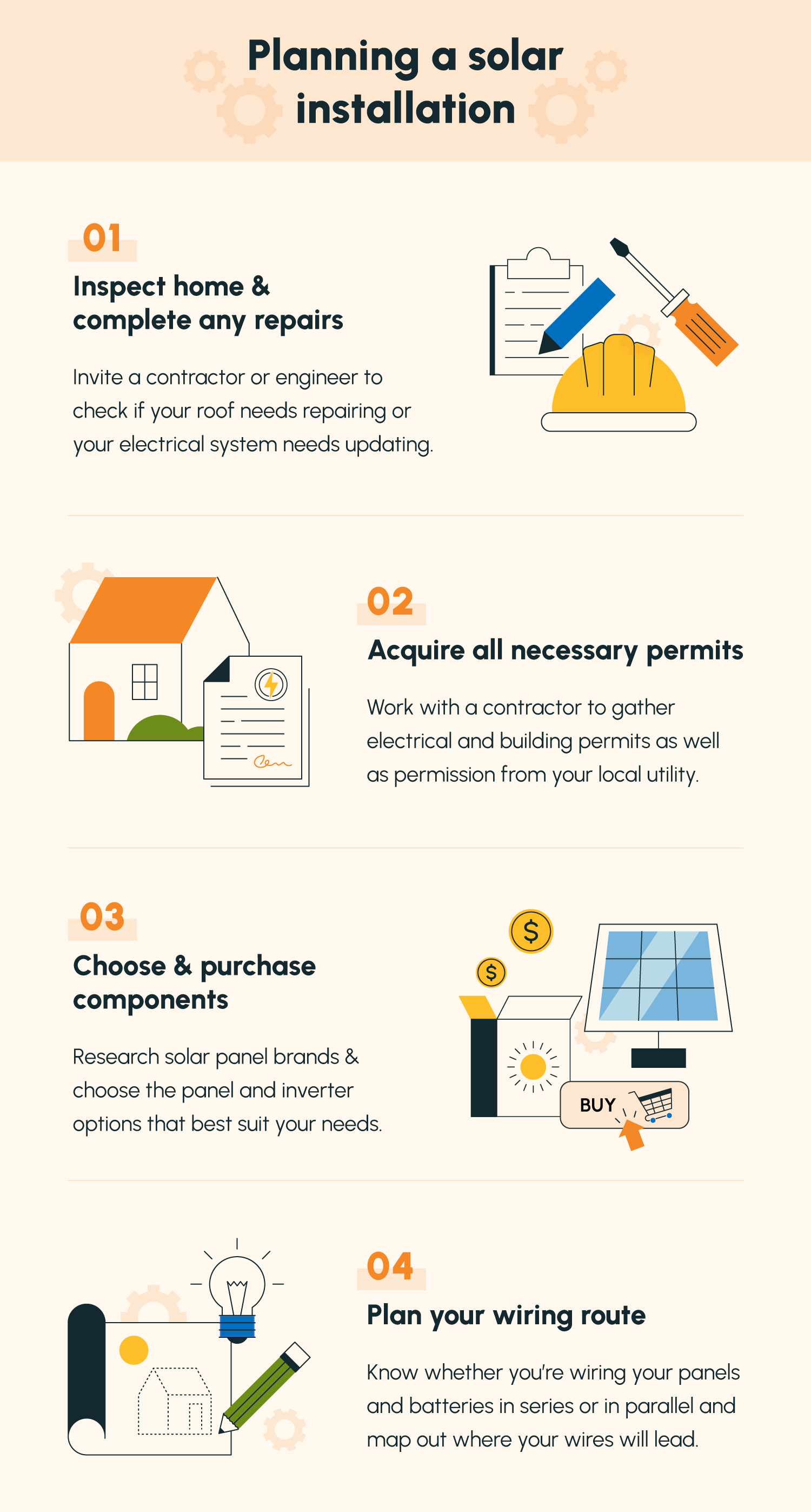
The solar panel installation process is straightforward, with professionals handling most of the work—but it helps to understand each step. It begins with a roof assessment to evaluate orientation, shading, and structural integrity. Next, homeowners should request and compare at least three quotes to find the best value and service. Once you’ve chosen a provider, review and sign the contract carefully, paying attention to warranty terms and system specifications.
After that, the installer secures necessary permits, which typically take two to four weeks. Installation itself happens in stages: mounting hardware is installed on day one, panels are secured on days two and three, and the wiring and inverter connections follow shortly after. The system is then tested to confirm proper power output and functionality. From start to finish, the entire process usually takes between one and three months. Your main responsibilities are to ensure the installation area is accessible and to stay in touch with your installer to monitor progress.
Handle Maintenance Tasks
Maintaining your solar panels is simple but essential for long-term performance. A little effort goes a long way in keeping your system efficient and reliable. Start by cleaning the panels every few months with a gentle hose rinse to remove dust and debris—this alone can boost energy output by 5–10%. Conduct a visual inspection once a year to ensure wiring and mounting components remain intact, and use your monitoring app to track performance or receive system alerts.
Plan to replace the inverter after 10–15 years, as it’s one of the few components that may wear out over time; replacement costs typically range between $1,000 and $2,000. Most solar panels come with warranties guaranteeing at least 80% power output after 25 years, giving homeowners confidence in long-term savings. In fact, one Florida homeowner reported a 15% efficiency gain simply after cleaning their panels. To stay consistent, set calendar reminders for maintenance and always hire professionals for any work involving roof heights or electrical components.
Address Common Challenges
Even with careful planning, solar installations can encounter a few bumps along the way—so it’s best to prepare in advance. Shade is one of the biggest challenges; untrimmed trees or nearby structures can cut your system’s energy output by 20–50%, so ensure panels receive ample sunlight. Homeowners’ association (HOA) rules can also be a hurdle, as some communities restrict or regulate panel placement, making it important to review bylaws before installation.
Delays can occur when connecting to the grid, since utility approvals often take several weeks. Adding battery storage increases system complexity and may require extra permits or wiring adjustments. Financing, too, can be tricky—high-interest solar loans can erase long-term savings if not carefully reviewed. The best way to avoid these pitfalls is through research: read installer reviews, verify certifications, and choose reputable providers who handle paperwork, permits, and approvals efficiently.
Learn from Real Homeowners
Real-life stories reveal the true impact of going solar. John in Arizona installed an 8kW system and saved $1,800 in his first year, expecting full payback in just six years. Mary in New York, despite heavy snow, found her panels still produced 90% of their usual winter output. In California, one family added battery storage and was able to power their home seamlessly during outages. These experiences reflect a larger trend—by 2025, over one million U.S. homes had adopted solar energy. The question is, what will your story be? Start with a simple home energy audit and see how solar could reshape your power and savings.
Explore System Types
Choosing the right solar setup comes down to what fits your home and lifestyle best. If you want the simplest and most affordable option, a grid-tied system is ideal—it connects to the utility grid so you can sell unused power back and lower your bills. Prefer full energy independence? An off-grid system lets you go completely self-sufficient, though it requires batteries and a bigger upfront investment. A hybrid system strikes a balance between both, storing extra energy for later use while still staying connected to the grid for reliability.
For most homes, a 6–10kW grid-tied system does the job well. As a quick guide, if your home uses around 10,000 kWh of electricity per year, a 7kW system should cover your needs comfortably. The best way to find your perfect setup is to play around with a few online solar calculators—they’ll help you see what system size matches your energy habits and budget.
Boost Home Value
Adding solar panels can give your home a serious value boost. They don’t just cut your energy bills—they make your property more attractive to buyers. In fact, research shows that homes with solar panels often sell for about 4% more than similar homes without them. Appraisers also consider the long-term savings solar provides, with one study estimating that each kilowatt of installed solar adds roughly $5,900 in value. Marketing your home as energy-efficient and eco-friendly can make it stand out in today’s housing market. The only question is—do buyers in your area appreciate the value?
Plan for Future Upgrades
Stay ahead as technology evolves.
Solar systems aren’t set in stone — you can upgrade anytime.
Battery prices drop about 10% every year, so adding one later makes sense.
When newer, more efficient panels hit the market, simply swap them in.
If you’re planning for an electric vehicle, consider integrating an EV charger into your solar setup.
And keep an eye on new breakthroughs — perovskite cells are already hitting 25% efficiency.
Set aside a small upgrade fund each year to keep your system future-ready and performing at its best.
Answer Key Questions
A typical 20-panel solar system requires about 400 square feet of roof space. Even on rainy days, panels still generate around 10–20% of their usual power. Most solar setups come with a 25-year performance warranty, ensuring long-term reliability. Financing options are also flexible, with many providers offering 0% interest loans to make installation more affordable. Maintenance is minimal, averaging just $150 per year, while the return on investment can range between 10–20% annually, depending on your energy usage and local sunlight conditions.
Take Action Steps
Ready to Go Solar? Follow These Steps:
-
Audit your energy bills – Calculate your average monthly electricity usage.
-
Research incentives – Check the DSIRE database for local rebates and tax credits in the USA
-
Schedule a site assessment – Many installers offer this free of charge to evaluate your roof’s solar potential.
-
Compare quotes – Review multiple offers and focus on warranty terms and equipment quality.
-
Install your system – Choose a trusted, certified installer for proper setup.
-
Monitor performance – Track your system closely during the first month to ensure optimal operation.
-
Track savings – Observe reductions in your energy bills and adjust habits for better efficiency.
-
Start small (optional) – Try portable solar panels first if you want to test the technology before full installation.
Your home can run on clean solar power — just take it one smart step at a time.



